In this post we shall provide an Introduction to Medical Writing, its types and scope in today’s medical world and the in the clinical research industry.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Medical Writing
- Medical writing vs Literary writing
- History of Medical writing
- Types of Medical writing
- Qualifications and Skills
- Informal Medical training
- Characteristics of Good Medical writing
- Medical writing Organizations
- Scope of Medical writing
- Sub-Specialisation in Medical writing
- Future of Medical writing
- You may be interested in…
- Diploma in Medical Writing
- Diploma in Medical Journalism
Introduction to Medical Writing
Medical writing is defined as communicating clinical and scientific data for a varied audience. This audience may include physicians, nurses, allied health professionals, pharmaceutical companies, scientists and even the general public.
Despite the variety of readers, medical writing is an activity which involves writing scientific information in a logical and precise manner.
According to Silvia Rogers, Phd. its main purpose is to record data obtained through research.This research could include that of journals, websites, peer reviewed articles, books etc.
Medical writing vs Literary writing
Medical writing differs from literary writing.
‘Literary writing is an art based on principles of personal style, fiction, and originality.’ It’s success largely depend on the creative imagination of the author.
However medical writing is often considered a craft as it requires certain skills, to communicate scientific data in a logical manner. It involves little room for creativity and builds on skills required for effective communication of scientific data.
History of Medical writing
The history of medical writing can be divided into three ages namely:
Age I – when medicine and writing became linked. Ancient medical texts have recorded beliefs and traditions of various medical institutions of the past.
Age II – when medical physicians became authors and began writing and spreading information through their literature. Medicine was now not only recorded but written and exchanged.
Age III – when writing included scientific development. This development led to all experimentation and evidence to be published and made available to the public.
Age IV – when medical writing finally became more sophisticated and required incorporating multimedia, sounds and pictures.
Age III ushered in a new era for medical writing. During this period the first scientific journal was published in the early 1600’s. Following this Louis Pasteur established his IMRD (Introduction, Methods, Results, Discussion). This was an introduction to formatting and publishing all scientific experimentation and discourse.Style manuals and books were prescribed for publishing scientific material. Publication became an integral final step of research. Any research that was not published was void. During and after World War II medical writers were no longer physicians.
Age IV is the period post 2000. At this stage evidence based medicine came to be established. With the advent of new technology, reporting research and its interpretation required more accuracy and analysis. Medical literature now came to include sounds, pictures, videos, graphs, charts and various new formats to make it more vibrant. Patient and physician education materials became more detailed and informative.
Types of Medical writing
Medical writing is broadly divided into two namely educational or academic medical writing and marketing medical writing.
Educational or academic medical writing
This is usually taken up by health professionals involves writing about various diseases and clinical conditions. Most health practitioners, present research and findings about varied clinical situations in journals, articles and books. With their science backgrounds, they learn to write about medicine. This forms the bulk of academic medical writing.
Marketing medical writing
This type of writing is often taken by graduates in journalism or literature graduates and involves writing about development of drugs and creating content for pharmaceutical companies. With their literary background, they learn medicine as they write.
Regulatory writing
This writing includes preparing a range of documents for regulatory submissions, including protocols and final reports for clinical trials, and clinical expert reports. They may also involve preparation of manuscripts for publication in medical journals. This is usually required by pharmaceutical companies to get their products registered with international regulatory authorities.
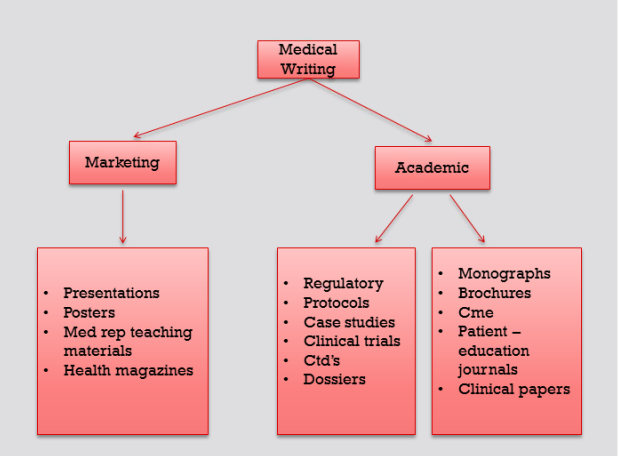
As discussed earlier, this flow chart explains various writing materials prepared in medical writing.
Marketing medical literature often includes presentation, posters, teaching materials for medical representatives, health magazines, etc.
Regulatory writing for pharmaceutical companies, includes preparing protocols, dossiers, case studies, clinical trial reports and common technical documents (CTD’s).
Academic medical literature also involves preparing continuing medical education materials, brochures, newsletters, journals, scientific papers and peer reviewed articles. The list is endless.
Qualifications and Skills
The qualifications for medical writing are varied. However, a degree in a life science would be extremely beneficial.
As of 2004, 65% of medical writers at the American Medical Writers’ Association had a masters’ or doctorate degree. And almost 50 % of them had a science background.
Apart from the qualifications, certain skills need to be developed and honed. These include good writing and word processing skills. As a writer it is important to ensure literature that is free from grammatical errors.
The ability to communicate effectively with others sometimes over long distances becomes necessary and is often a challenge for new writers.
Marketing any medical information requires thorough research and attention to small details, either in print or media. Most medical writing assignments are adherent to specific time frames. Being oriented to a deadline and fulfilling them is a skill that needs to be mastered.
Informal Medical training
In an effort to train oneself in medical writing, its important to be in the know of new medical and pharmaceutical developments by subscribing and reading newly published medical literature. Most medical reports involve statistics , understanding basic statistics can help especially while preparing reports and protocols.
Various institutions require different writing style guides and formats. Familiarize yourself with the different styles namely APA, Harvard etc. Update yourself with FDA and other medical regulating bodies and their guidelines. Using computer software with ease is an advantage to medical writers, updating skills in computers can help you become more efficient.
Characteristics of Good Medical writing
A good medical writer should be :
Thoroughly researched: Any article, presentation or medical content should be researched well with the most recent representation of the content and its findings as far as its possible.
Accurate: It should be accurate and precise so that readers can arrive at a conclusion after what they have read.
Logically organized: Since most sciences are based on logic it is important for writers to demonstrate a logical train of thought as they write.
Readable: It should be easy to read without any complicated language or terms. The content written must reflect a coherent thought process.
Credible: Good medical writing should also be written convincingly in terms of concept, style and language so that readers find it credible.
Efficient: By improving skills it can be written efficiently using all the tools of moderns technology so as to present scientific data.
Transparent: One of the most important characteristics is transparency. Good medical content is transparent and simple not confusing and vague.
Medical writing Organizations
Currently there are four medical writing organizations that train and organize lectures and seminars for medical writers. They provide forums or platforms for medical writers to learn from each other. India also now has an organization of its own namely the Indian Medical Writers’ Association (IMWA).
The others being the American Medical Writers’ Association (AMWA), European Medical Writers’ Association (EMWA) and Australasian Medical Writers’ Association (AMWA).
Scope of Medical writing
For medical writers today the scope is vast. Depending on your qualifications and skills medical writers can take up a role as any of those mentioned below:
- Public Affairs or Public communications associate
- Publications specialist, Coordinator, Manager or Director
- Regulatory Affairs or regulatory compliance associate
- Science writer, Science Editor
- Technical writer, Technical editor
- Web Content Administrator
As one gains experience, the position becomes more specialized and focused. Publications specialists, Regulatory Affairs Associates and Medical editors are writers who have spent years on the job.
One might begin asking where are medical writers needed?
Medical writers are now needed at advertising agencies, contract research organizations, government agencies, hospitals and other health care centers. Since its conception the medical writing field has been constantly growing with more and more institutions looking to hire them.
Many pharmaceutical companies, medical schools and associations also need medical writers to help market drugs and report risk/ benefits of the same.
Biotechnology companies and medical diagnostic companies also rely on medical literature to create awareness regarding breakthroughs in medical technology.
With media now encompassing the television, radio and internet the scope of medical writing has increased by leaps and bounds thus making it a vibrant and dynamic field to work in.
Sub-Specialisation in Medical writing
Depending on one skill and interest one can develop writing in a particular division thus gaining experience and expertise on the subject.
Regulatory writing can be subdivided into preparing documents for regulatory submission of drugs, case narratives, clinical study reports, periodic update safety reports, patient information leaflets value dossiers and investigative brochures.
You can focus your attention on creating content only for websites, journals, or brand development of different drugs.
Future of Medical writing
In the future medical writing is likely to become more specialized. As communication techniques, become more sophisticated, it will allow more specialization.
Also as more research comes to be published, new formats for print and electronic coding may come into place thus formalizing the way medical literature is prepared and written.
Since the medical writing is growing exponentially, it would become necessary to establish programs that could teach and mentor students in the field. With the sub-specialization of science and medicine, medical writers will increasingly be pressured to focus on diversifying into a particular subject or format.
Want to explore a career in Medical writing? Join our Diploma in Medical Writing program and kick-start a career in Medical and Scientific writing.
Already completed a program in Medical writing. Enhance your expertise on the subject by subscribing to our Diploma in Medical Writing course to get access to a wealth of knowledge on the subject on our learning portal.
You may be interested in…